Corporate Growth with AI

The Appleton Greene Corporate Training Program (CTP) for Corporate Growth with AI is provided by Mr. McAdam Certified Learning Provider (CLP). Program Specifications: Monthly cost USD$2,500.00; Monthly Workshops 6 hours; Monthly Support 4 hours; Program Duration 12 months; Program orders subject to ongoing availability.

Personal Profile
Mr. McAdam is a “been there and done that” hired CEO, serial entrepreneur, and investor who serves as a “hands on” private business advisor to CEOs who want to double their bottom line.
As a serial entrepreneur, Mr. McAdam has successfully founded a mergers & acquisitions advisory firm, an investment organization, a real estate holding company, a computer company, and a consulting organization, among others. Mr. McAdam continues to form a reputation for offering experienced-based strategic, tactical, pragmatic, and money- making guidance.
He is a Wharton MBA and was an Instructor at The Wharton Small Business Development Center in Strategic Business Planning for thirteen years, where he educated adult entrepreneurs with no formal business training across all industries on effective strategic business planning and optimal execution.
Regarding Artificial Intelligence (AI), John stands at the forefront, navigating the intricate landscape of AI and its transformative impact on corporate growth. He stays ahead of the AI curve, by tracking the latest advancements in AI and uncovering cutting-edge applications for corporate growth. Drawing from the prestigious “AI at Wharton” program and leading sources, John delves deep into leading research, ensuring that every strategy and decision is rooted in the latest and most reliable insights. With him, you’re not just keeping up — you’re setting the pace.
With an investment portfolio spanning over twenty AI companies, John isn’t just an observer — he’s an active participant in shaping the future of AI. This culmination of avant-garde AI insights and decades of experiences with Corporate Growth enables John to deliver unparalleled corporate growth value for his clients.
John’s passion lies in empowering business owners and executives to harness the full potential of AI to make business better. Whether it’s buying a company, optimizing processes, unlocking new revenue streams, or enhancing customer experiences, he’s dedicated to helping you excel in every aspect of your business journey.
To request further information about Mr. McAdam through Appleton Greene, please Click Here.
(CLP) Programs
Appleton Greene corporate training programs are all process-driven. They are used as vehicles to implement tangible business processes within clients’ organizations, together with training, support and facilitation during the use of these processes. Corporate training programs are therefore implemented over a sustainable period of time, that is to say, between 1 year (incorporating 12 monthly workshops), and 4 years (incorporating 48 monthly workshops). Your program information guide will specify how long each program takes to complete. Each monthly workshop takes 6 hours to implement and can be undertaken either on the client’s premises, an Appleton Greene serviced office, or online via the internet. This enables clients to implement each part of their business process, before moving onto the next stage of the program and enables employees to plan their study time around their current work commitments. The result is far greater program benefit, over a more sustainable period of time and a significantly improved return on investment.
Appleton Greene uses standard and bespoke corporate training programs as vessels to transfer business process improvement knowledge into the heart of our clients’ organizations. Each individual program focuses upon the implementation of a specific business process, which enables clients to easily quantify their return on investment. There are hundreds of established Appleton Greene corporate training products now available to clients within customer services, e-business, finance, globalization, human resources, information technology, legal, management, marketing and production. It does not matter whether a client’s employees are located within one office, or an unlimited number of international offices, we can still bring them together to learn and implement specific business processes collectively. Our approach to global localization enables us to provide clients with a truly international service with that all important personal touch. Appleton Greene corporate training programs can be provided virtually or locally and they are all unique in that they individually focus upon a specific business function. All (CLP) programs are implemented over a sustainable period of time, usually between 1-4 years, incorporating 12-48 monthly workshops and professional support is consistently provided during this time by qualified learning providers and where appropriate, by Accredited Consultants.
Executive summary
Corporate Growth with AI
In the ever-evolving landscape of the business world, where competition is fierce, and the pace of innovation is relentless, organizations are constantly seeking new pathways to growth and business success. Amidst this quest, the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has opened up unprecedented opportunities for companies willing to embrace change and innovation. The program on “Corporate Growth with AI” stands at the confluence of strategic planning and technological advancement, offering a beacon of guidance for organizations aiming to not just survive and thrive in this new era.
At the heart of corporate growth lies a paradox: while expanding a business is inherently challenging, fraught with uncertainties and potential pitfalls, it is also essential for survival in today’s dynamic market environment. Navigating this complex terrain requires more than just a visionary leadership team; it necessitates a well-prepared management team equipped with the tools, knowledge, and strategic insight to steer the organization towards sustainable growth. This convergence is where the “Corporate Growth with AI” program comes into play, serving as a crucible where the alchemy of AI-driven growth strategies is meticulously crafted for your business.
The program is predicated on the understanding that growth can take multiple forms – be it organic expansion, strategic acquisitions, or a hybrid approach combining both elements. However, the unifying factor across all these avenues is the pivotal role of AI. In an age where data is the new currency, AI emerges as an exceptional resource tool, providing organizations with the means to analyze market trends, optimize operations with human leadership, and generate content to create competitively distinctive strategies. By integrating AI into the fabric of their strategic planning, businesses can unlock a level of efficiency, innovation, and market responsiveness previously unavailable until now.
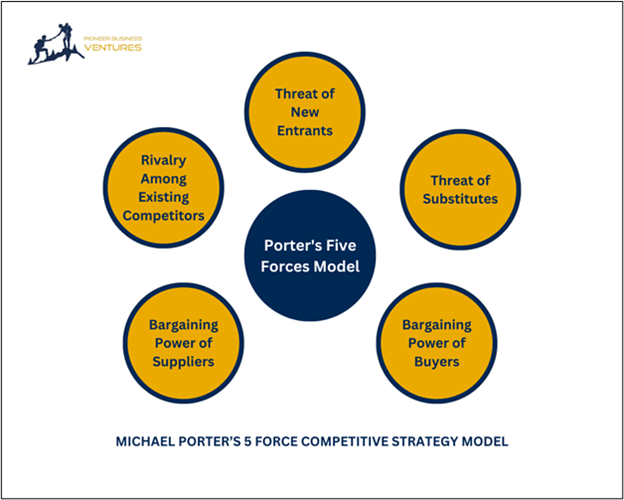
Michael Porter’s 5 Force Competitive Strategy Model
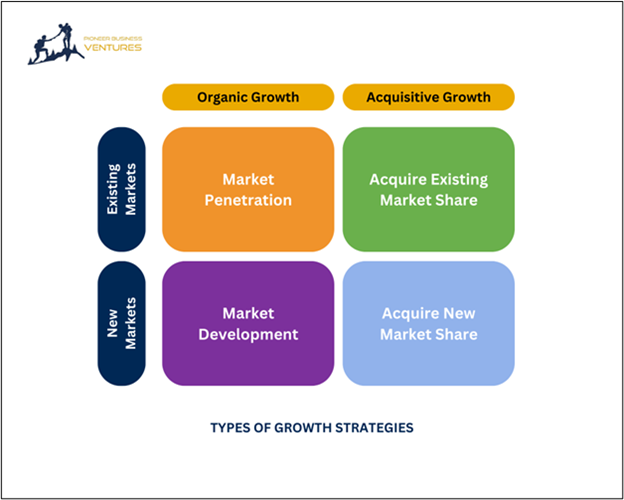
Types of Growth Strategies
Leadership and management training form the cornerstone of this transformative journey. The program emphasizes the critical importance of nurturing a leadership mindset that is adaptive, forward-thinking, and receptive to leveraging AI for strategic advantage. It is about cultivating a culture where managers and supervisors are not just administrators but visionaries who can foresee the potential of AI and apply insights to revolutionize their industry. Through a curriculum that blends peer-reviewed AI research with practical applications, participants are equipped to lead their teams confidently while navigating the complexities of corporate growth with agility and insight.
The bespoke nature of the program ensures that the strategic business planning process is not a one-size-fits-all proposition but is instead tailored to align with the unique strengths and challenges of each organization tailored to align with each organization’s unique strengths and challenges. This personalized approach not only saves invaluable time and financial resources but also enhances the effectiveness of growth strategies, ensuring they are deeply resonant with the organization’s core objectives and market positioning.
Furthermore, the program addresses the essential aspect of expectation management and communication, preparing teams for the multifaceted challenges of growth. By setting clear expectations and fostering an environment of transparent communication, organizations can ensure that their growth journey is cohesive, aligned, and imbued with a sense of shared purpose.
In conclusion, the “Corporate Growth with AI” program is more than just a training program; it is a transformative experience that prepares organizations for the future of business. By harnessing the power of AI, embracing strategic planning, and cultivating leadership excellence, participants are not just ready for growth; they are poised to redefine the boundaries of what is possible in their respective industries. As we stand on the brink of a new era of corporate growth, the question is no longer if AI will be integral to business strategies, but how swiftly and effectively organizations can adapt to this new paradigm.

Overcoming Growth Challenges: The Role of AI in Corporate Expansion
Corporate growth, especially in the digital age, comes with its unique set of challenges. Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents itself as a transformative solution to many of these pain points, offering innovative ways to navigate the complexities of expansion and competition. Here are ten common pain points organizations face that Corporate Growth with AI can help address:
1. Data Overload: Organizations often struggle to manage and make sense of the vast amounts of data their operations generate. AI can process this data more efficiently than traditional methods, providing actionable insights and helping businesses make informed decisions.
2. Customer Experience and Personalization: Personalizing customer experiences is crucial for retention and satisfaction in todays markets. AI enables organizations to tailor their services and products to individual customer preferences, improving engagement and loyalty.
3. Operational Inefficiencies: This training enables business leaders to utilize AI to streamline operations, automate routine tasks, and optimize logistics and supply chains, reducing costs and improving efficiency. Subsequently, the program enables businesses to allocate resources more effectively and focus on priority strategic growth areas.
4. Innovation and Product Development: Staying competitive often requires rapid innovation and the development of new products. AI can accelerate the R&D process, from initial concept to market readiness, by enabling leaders to predict trends, simulate outcomes, and optimize design processes.
5. Market Adaptation and Flexibility: Quickly adapting to market changes is a significant challenge. A can monitor competitors to prepare you better to forecast market trends and shifts in consumer behavior, enabling businesses to pivot strategies proactively.

6. Talent Acquisition and Management: Finding and retaining the right talent is crucial for growth. Keeping employee turnover low during an accelerated business growth phase is essential. AI-driven HR tools can enhance recruitment processes, identify skills gaps, and support employee development, helping organizations build a workforce that drives growth.
7. Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks, from financial uncertainties to cybersecurity threats, is a constant challenge. AI can provide advanced risk assessment tools, monitor for potential threats, and suggest mitigation strategies, enhancing an organization’s resilience.
8. Scaling Challenges: As organizations grow, scaling operations efficiently can become a bottleneck. AI solutions can help business leaders see how others manage scaling complexities such as automating processes and best practices. This provides insights into efficient resource allocation.
9. Customer Insights and Market Intelligence: Understanding customer needs and buyer decision-making is critical for growth. AI can analyze customer feedback and market data in real-time, offering deeper insights into consumer preferences and competitive landscapes.
10. Regulatory Compliance and Governance: Navigating the maze of regulatory requirements, especially in global markets, can be daunting. AI can monitor regulatory changes, ensure compliance across operations, and reduce the risk of penalties or legal issues.
Incorporating AI into corporate growth strategies offers a way to address these business risks more effectively, transforming challenges into opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage. By leveraging AI’s capabilities, organizations can enhance decision-making, improve operational efficiencies, and create more personalized and engaging customer experiences, all of which are critical for sustainable growth in the modern business environment.

Strategic Advantages: Unleashing Corporate Growth through AI
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into corporate growth strategies offers a myriad of benefits that extend beyond addressing operational bottlenecks and silos. These advantages underscore the transformative potential of AI in redefining how organizations approach expansion and competitiveness. Here are the main benefits of leveraging AI for corporate growth:
Enhanced Decision-Making
AI’s ability to rapidly process and analyze large datasets rapidly provides executives with deep insights, enabling more accurate and informed decision-making. This capability is crucial for strategic planning, market entry decisions, and investment allocations.
Talent Optimization
Quality recruiting helps organizations employ the best talent in the market to implement growth. A quality talent optimization formula typically includes talent optimization software plus an Applicant Tracking System (ATS) in conjunction with AI to recruit the best and the brightest talent the organization can afford. These systems don’t stop there. It is time to get the right people on the right teams to optimize corporate growth. These three systems, coordinated by informed HR leadership, empower the organization to excel.
Predictive Analytics for Forecasting:
AI excels in monitoring and gathering vast amounts of data sets to enable corporate leaders to forecast better market trends, consumer behavior, and potential market shifts. Organizations can use these insights to anticipate future demands, adapt strategies ahead of time, and seize market opportunities, ensuring they stay ahead of competitors.
Dynamic Pricing Strategies:
AI algorithms can dynamically recommend price adjustments based on market demand, competition, and consumer behavior, maximizing revenue opportunities without sacrificing customer satisfaction. This approach allows for more flexible and responsive pricing strategies that can adapt to changing market conditions.
Productivity Gains through Automation:
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI frees up human resources to focus on higher-value activities. This shift boosts productivity and enhances employee satisfaction by reducing burnout associated with mundane tasks.
Customer Service Excellence:
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 customer service, handling inquiries and resolving issues promptly. This level of service excellence improves customer satisfaction and loyalty, contributing to long-term growth.
Innovative Product and Service Development:
AI can identify emerging trends and gaps in the market by informing business leaders of the development of innovative products and services in their respective markets. This proactive approach to innovation keeps companies relevant and competitive.
Supply Chain Optimization:
AI can optimize supply chain operations by enabling logistics leaders to predict demand, identify potential disruptions, and suggest alternative suppliers or routes. This optimization reduces costs, improves efficiency, and ensures the timely delivery of products.

Enhanced Security Measures:
AI’s role in cybersecurity is invaluable, as it can detect and respond to threats faster than traditional methods. By securing data and operations, AI helps maintain customer trust and protect the company’s reputation.
Global Expansion Support:
AI tools can analyze global markets, cultural trends, and regulatory environments, providing insights that support informed decisions about international expansion. This capability is crucial for organizations looking to grow beyond their home markets.
Sustainability Initiatives:
AI can help companies achieve their sustainability goals by optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and improving energy efficiency. These efforts contribute to environmental stewardship but also resonate with increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Sales and Marketing Process Improvements
Acquiring new customers is essential for business growth. With an active human interface, AI can improve sales and marketing processes by supporting lead generation, market segmentation, salient purchasing attributes, and best practices for sales operations. Customer service is quickly becoming automated via AI.
Incorporating AI into corporate growth strategies offers a comprehensive suite of benefits that can propel organizations to new heights of efficiency, innovation, and market responsiveness. By harnessing the power of AI, companies can unlock new avenues for growth, adapt to the rapidly changing business environment, and establish a strong foundation for long-term success.
Curriculum
Corporate Growth with AI – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Management Assessments
- Part 1 Month 2 Organization Strategy
- Part 1 Month 3 Sales and Marketing
- Part 1 Month 4 Competitive Assessment
- Part 1 Month 5 Milestone & Action Planning
- Part 1 Month 6 Financial Management
- Part 1 Month 7 Acquisitive Growth
- Part 1 Month 8 Human Resources Management
- Part 1 Month 9 Operations Planning
- Part 1 Month 10 Information Systems
- Part 1 Month 11 Anticipating Growing Pains
- Part 1 Month 12 Year-End Presentations
Program Objectives
The following list represents the Key Program Objectives (KPO) for the Appleton Greene Corporate Growth with AI corporate training program.
Corporate Growth with AI – Part 1- Year 1
- Part 1 Month 1 Management Assessments – In the context of management interviews within a workshop, a trainer engages in 30-minute private one-on-one sessions with each participant. This structured interaction establishes a personalized understanding between the trainer and each manager. The trainer aims to uncover individual goals, expectations, and areas for improvement that participants wish to address through the workshop series. These interviews serve as a foundational step, allowing for tailored introductions, thorough assessments of managerial competencies, AI learning stage, and strategic refinements to the workshop content. The assessments ensure that the workshop’s objectives are aligned with each manager’s unique developmental needs; enhancing the training program’s effectiveness and impact.
- Part 1 Month 2 Organization Strategy – The organization’s business strategy leverages AI as a research assistant to drive corporate growth. This approach harnesses artificial intelligence to analyze market trends, identify opportunities, optimize operations, and inform strategic decisions. By integrating AI into its core processes, the organization enhances efficiency, fosters innovation, and maintains a competitive edge in its industry.
- Part 1 Month 3 Sales and Marketing – This month, we delve into how AI can catalyze corporate growth in sales, marketing, advertising, and public relations. AI’s role is pivotal in enriching customer insights, enabling businesses to understand and anticipate consumer behavior more effectively. It personalizes marketing campaigns, ensuring that messages resonate with the intended audience. In advertising, AI optimizes targeting, ensuring that ads reach the most relevant viewers, maximizing engagement and ROI. Moreover, AI significantly enhances precision, efficiency, and impact in sales and marketing through these avenues..
- Part 1 Month 4 Competitive Assessment –
In Month 4, the focus shifts to the integral role of AI in competitive assessment, highlighting how businesses can employ artificial intelligence to dissect and understand market trends, competitor maneuvers, and consumer preferences. This advanced analytical capability allows companies to decipher complex market dynamics, offering a granular view of their competitive landscape. By leveraging AI, businesses can unearth valuable insights about their rivals’ strategies, detect emerging market opportunities, and pinpoint potential threats. Such profound intelligence empowers firms to make informed, strategic decisions, securing a formidable position in their industry and ensuring they stay ahead in the competitive race. - Part 1 Month 5 Milestone & Action Planning – In Month 5, the emphasis is on employing AI to establish milestones and craft action plans for corporate growth. This phase underscores how artificial intelligence tools can be pivotal in forecasting future trends, setting achievable goals, and formulating strategic actions. Leveraging data analytics and predictive modeling, AI provides a robust framework for decision-making, enabling businesses to outline precise and actionable steps towards their objectives. By integrating AI into the planning process, companies can ensure that their strategies are data-driven, targeted, and optimized for efficiency, significantly enhancing the likelihood of meeting their desired outcomes effectively and within set timelines.
- Part 1 Month 6 Financial Management – Month 6 delves into the transformative impact of AI on financial management, particularly focusing on business funding and capital expenditure (CAPEX). It highlights how AI technologies can revolutionize financial planning by providing deeper insights and more accurate forecasts. AI’s advanced analytical capabilities enable businesses to make more informed investment decisions and optimize capital allocation processes. By integrating AI into financial management, companies can enhance their financial operations’ efficiency, ensuring better resource management, and support sustainable corporate growth. AI aids in identifying strategic investment opportunities, ultimately contributing to a more robust and forward-thinking financial strategy.
- Part 1 Month 7 Acquisitive Growth – The discussion on acquisitive growth through the AI lens reveals how companies can harness artificial intelligence to scout and evaluate potential acquisition targets. AI can analyze vast datasets to identify companies that align with strategic growth objectives and assess, their financial health, market position, and compatibility. Moreover, AI enhances the due diligence process, offering deeper insights and predictive analytics to forecast the potential success of an acquisition. By employing AI in these critical phases, businesses can make more informed decisions, ensuring that their mergers and acquisitions are strategically sound and value-adding, thereby maximizing the effectiveness of their acquisitive growth strategies.
- Part 1 Month 8 Human Resources Management – This exploration focuses on integrating AI into human resources management and corporate governance as a catalyst for corporate growth. AI revolutionizes HR processes by automating routine tasks, enhancing talent acquisition efficiency, and bolstering retention strategies. It provides deep insights into employee engagement, helping companies understand and respond to their workforce’s needs more effectively. Additionally, AI is crucial in ethical governance, automating compliance monitoring and ensuring adherence to regulations and corporate standards. By embedding AI in these key areas, organizations can foster a culture that aligns with their growth objectives, ensuring that their human resources strategies are as advanced and dynamic as their business ambitions.
- Part 1 Month 9 Operations Planning –
This segment explores the integration of AI in operations planning and quality control, underscoring its potential to fuel corporate growth. By leveraging AI-driven analytics and automation, businesses can significantly refine operational efficiency, elevating product quality and ensuring consistency in service delivery. AI tools analyze data in real-time, providing actionable insights that enable swift adjustments to operational processes, enhancing productivity and reducing waste. Furthermore, AI’s predictive capabilities can foresee potential issues in quality control, allowing preemptive actions to maintain high standards. This strategic use of AI fosters continuous improvement and scalability in a company’s core operations, vital for sustained growth and competitiveness. - Part 1 Month 10 Information Systems –
This section highlights the pivotal role of AI-powered information systems in fostering corporate growth. These advanced systems collect, analyze, and leverage data to inform strategic decision-making. Providing deep insights and predictive analytics enables businesses to enhance operational efficiencies and spur innovation. AI-driven information systems facilitate the identification of trends and patterns, supporting companies in swiftly adapting to market changes and staying ahead of competitors. This integration of AI into information systems ensures that organizations are agile, data-informed, and equipped to maintain a competitive edge in the fast-evolving business landscape. - Part 1 Month 11 Anticipating Growing Pains – This segment delves into the critical aspect of anticipating and managing the growing pains that accompanying corporate expansion. Utilizing AI-driven insights and real-world case studies, it sheds light on effective strategies to foresee and address potential scalability challenges, cultural shifts, and operational hurdles. The focus is on how AI can provide predictive analysis, offering foresight into potential issues and enabling proactive strategies to mitigate them. By leveraging AI for strategic planning and operational adjustments, businesses can smoothly navigate growth phases, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle expansion challenges and paving the way for sustained long-term success.
- Part 1 Month 12 Year-End Presentations – This section emphasizes the crucial role of year-end presentations in articulating corporate growth, particularly in the context of AI integration. It illustrates how businesses can harness data analytics and AI-generated insights to comprehensively report annual progress, spotlight key achievements, and chart out future growth strategies. These presentations are pivotal in demonstrating value to stakeholders, promoting transparency, and establishing a narrative of success and vision for the future. They facilitate informed decision-making and secure continued investment in AI-driven initiatives, underpinning the organization’s commitment to innovation and sustained growth.
Methodology
Corporate Growth with AI
Incorporating AI into corporate growth strategies involves a blend of methodologies, standard processes, and business practices. These methodologies are designed to integrate AI capabilities seamlessly into various facets of an organization, enabling enhanced decision-making, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage. Here’s an overview of common business processes and methodologies used in corporate growth with AI:
Data-Driven Decision Making
In the realm of corporate growth and innovation, data-driven decision-making stands as a cornerstone strategy, propelled by the advancements in Big Data Analytics and Predictive Analytics. These methodologies empower organizations to navigate the complexities of the market with precision and foresight, transforming raw data into a strategic asset.
Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics plays a pivotal role by enabling businesses to sift through vast, diverse datasets to identify patterns, trends, and insights. In an era where data is generated from multiple sources at an unprecedented scale, the ability to aggregate, process, and analyze this data offers a competitive edge. Organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations, customer behavior, and market dynamics. This holistic view facilitates informed strategic decisions, from optimizing operational efficiencies to tailoring marketing campaigns and beyond. Moreover, Big Data Analytics allows companies to identify new opportunities for innovation and growth, ensuring that strategies aligned with actual market needs and customer desires.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive Analytics further enhances data-driven decision-making by employing statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes based on historical data. This proactive approach enables businesses to anticipate market trends, consumer behavior changes, and potential risks, allowing for strategic adjustments before challenges or opportunities fully materialize. For example, predictive analytics can forecast demand for products and services, helping companies optimize inventory levels and production schedules to meet market demand efficiently. It can also identify potential customer churn, enabling targeted interventions to improve retention rates.
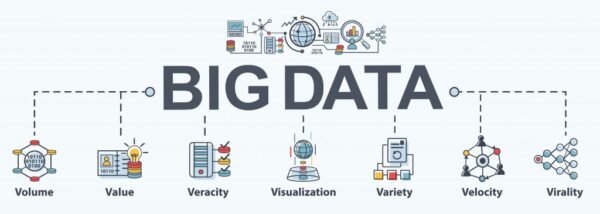
Together, Big Data Analytics and Predictive Analytics revolutionize how organizations approach decision-making. By moving from intuition-based to data-driven strategies, businesses can significantly increase their accuracy in planning and execution. This transition mitigates risks and maximizes the potential for growth and profitability in an increasingly competitive and complex marketplace.
Process Automation and Optimization
Process Automation and Optimization represent transformative elements in pursuing corporate efficiency and competitive advantage. Organizations can significantly enhance productivity and streamline workflows by integrating Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI-driven process improvement into their operations.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a powerful tool for automating routine and repetitive tasks across various business functions, from finance and HR to customer service and beyond. RPA works by deploying software robots or “bots” that mimic human actions to complete tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, or customer query handling. This speeds up processes, increases accuracy by reducing human errors, ad frees employees to focus on more strategic, value-added activities. RPA can lead to substantial cost savings and operational efficiencies, making it a critical component of digital transformation strategies for businesses seeking to maintain a competitive edge.
AI-Driven Process Improvement
AI-Driven Process Improvement takes automation a step further by leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence to analyze and optimize business processes. Unlike RPA, which automates tasks based on predefined rules, AI-driven process improvement continuously learns from data and user interactions to identify inefficiencies, suggest improvements, and even predict future process outcomes. This can include optimizing supply chain logistics, enhancing customer service through predictive analytics, or improving product quality by identifying real-time manufacturing defects. AI’s capability to adapt and improve processes over time can lead to unprecedented levels of efficiency and effectiveness, driving significant productivity and operational excellence improvements.
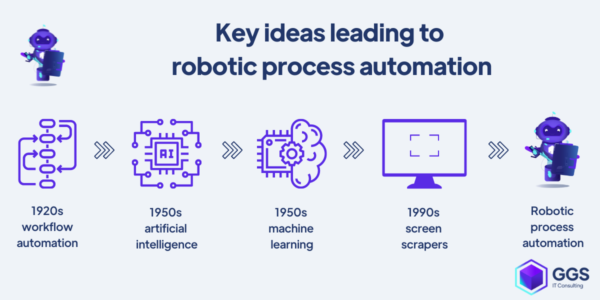
RPA and AI-driven process improvement offers a dual approach to revolutionizing business operations. By automating routine tasks and optimizing processes through intelligent analysis, organizations can achieve higher level of operational efficiency, reduce costs, and free up resources to focus on innovation and growth. This strategic technology integration enhances operational capabilities and positions businesses for future success in an increasingly digital world.
Customer Insights and Personalization
• Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): Integrating customer data from multiple sources into a unified platform for a comprehensive view of customer behavior and preferences.
• Personalization Engines: Utilizing AI to deliver personalized customer experiences to customers across various touchpoints, enhancing engagement and loyalty.
Market Analysis and Competitive Intelligence
• Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing customer feedback and market sentiment from social media and other sources to inform product development and marketing strategies.
• Competitive Intelligence Tools: AI monitors competitors’ activities and market dynamics, providing actionable insights for strategic positioning.
Innovation and Product Development
Innovation and product development are pivotal for companies aiming to stay competitive and meet evolving market demands. Integrating AI-driven research and development (R&D) alongside design thinking processes represents a forward-thinking approach to creating groundbreaking products and services.
AI-Driven R&D
AI-Driven R&D is revolutionizing how companies approach the innovation lifecycle. By harnessing AI algorithms, organizations can significantly accelerate the R&D process, from initial concept to product launch. AI’s capability to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds allows for the simulation and prediction of outcomes, enabling companies to iterate and refine concepts much more rapidly than traditional methods. This acceleration reduces the time to market for new products, providing a critical advantage in fast-paced industries. Furthermore, AI can uncover novel combinations of materials or identify patterns that might not be immediately apparent to human researchers, leading to innovative product features and functionalities.
Design Thinking
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that focuses on understanding the user’s needs and generating creative solutions to meet those needs. Integrating AI into the design thinking process can enhance this creativity, providing designers and developers with tools that offer insights into customer behavior, preference trends, and potential design pitfalls. AI can analyze user feedback in real-time, suggesting modifications that might improve the user experience or highlighting features that customers particularly value. This integration of AI not only streamlines the design process but also ensures that the final products are more closely aligned with user expectations and market demands.
Together, AI-driven R&D and AI-enhanced design thinking form a powerful synergy that can significantly boost innovation and product development. By leveraging AI’s analytical and predictive capabilities, companies can speed up the innovation process and ensure their products and services are innovative, user-centric, and poised for market success.
Talent Management and Workforce Planning
Talent Management and Workforce Planning are critical components of an organization’s strategy to ensure it has the right people with the right skills at the right time. Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into these areas can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to attract, retain, and develop talent.
AI in Recruitment
AI in Recruitment is transforming how organizations approach hiring, making it more efficient and effective. AI tools can automate the screening of resumes, parsing through thousands of applications to identify candidates whose skills and experiences match the job requirements closely. This speeds up and minizes human biases, ensuring a more diverse and qualified candidate pool. Furthermore, based on historical data and predictive success modeling, AI-driven candidate matching algorithms can enhance the quality of hires by predicting which candidates are most likely to succeed in a role. This sophisticated approach to recruitment enables organizations to make more informed hiring decisions, improving the overall quality of their workforce.
Workforce Analytics
Workforce Analytics leverages AI to provide deep insights into various aspects of workforce management. By analyzing data on employee performance, engagement, turnover, and other metrics, AI can identify patterns and predict future staffing needs, by analyzing employee performance, engagement, turnover, and other HR metrics.. Moreover, AI can pinpoint skills gaps within the existing workforce, guiding targeted training and development programs. This proactive approach to talent development helps close the skills gap. It plays a crucial role in employee retention, as employees are likelier to stay with an organization that invests in their growth and development.
By harnessing the power of AI in Talent Management and Workforce Planning, organizations can achieve a competitive edge in the talent market. AI’s capabilities in enhancing recruitment processes and providing actionable insights through workforce analytics empower organizations to build a more skilled, engaged, and future-ready workforce.
Risk Management and Compliance
• AI for Risk Assessment: Leveraging AI to identify, assess, and prioritize risks, from financial risks to cybersecurity threats.
• Regulatory Compliance Monitoring: Utilizing AI to monitor and ensure compliance with changing regulations and standards across different jurisdictions.
Strategic Planning and Growth Modeling
Strategic Planning and Growth Modeling are crucial for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of today’s business landscape and capitalize on future growth opportunities. Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into these domains revolutionizes how companies forecast, plan, and execute their growth strategies.
Scenario Planning
Scenario Planning with AI introduces a dynamic and sophisticated approach to navigating uncertainty and preparing for multiple future possibilities. AI algorithms can simulate strategic based scenarios based on various internal and external factors, including economic conditions, market trends, and competitor actions. This capability allows leaders to visualize the potential outcomes of different strategies, weigh their options, and make more informed decisions. AI-driven scenario planning helps organizations anticipate changes, assess the impact of possible disruptions, and adjust their strategies proactively, ensuring resilience and agility in the face of volatility.
Growth Analytics
Growth Analytics leverages AI to delve deep into market, customer, and internal data, uncovering insights that drive strategic growth initiatives. AI tools can analyze patterns in customer behavior, market shifts, and performance data to identify untapped growth opportunities and areas for improvement. By providing a granular understanding of the factors that influence growth, AI-powered growth analytics enables organizations to tailor their strategies to better meet market demands and customer needs. Furthermore, AI can optimize resource allocation, targeting investments in areas with the highest potential for returns, thereby maximizing efficiency and effectiveness in achieving growth objectives.

Integrating AI into Strategic Planning and Growth Modeling enhances an organization’s ability to make data-driven decisions and foster a culture of innovation and forward-thinking. By leveraging AI for scenario planning and growth analytics, companies can gain a competitive edge, adapting their strategies to thrive in an ever-changing market landscape. This strategic incorporation of AI empowers organizations to pursue growth confidently, backed by insights that drive operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
Industries
This service is primarily available to the following industry sectors:
Healthcare
The healthcare industry is currently at a pivotal juncture, characterized by rapid technological advancements, evolving patient expectations, regulatory changes, and the ongoing challenge of managing costs while improving the quality of care. This complex landscape is further complicated by the global aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has accelerated the adoption of digital health technologies and catalyzed significant shifts in healthcare delivery models.
Technological Innovation and Digital Health: One of the most significant trends shaping the healthcare industry is the surge in technological innovation, particularly in the realms of digital health, telemedicine, and artificial intelligence (AI). The proliferation of wearable devices, mobile health apps, and remote monitoring tools has empowered patients to take a more active role in managing their health. Telehealth, which saw exponential growth during the pandemic, continues to be embraced by patients and providers for its convenience and potential to improve access to care. AI and machine learning are being leveraged to enhance diagnostic accuracy, personalize treatment plans, and optimize operational efficiencies within healthcare facilities.
Value-based Care and Patient-centricity: The industry is increasingly moving away from volume-based care to value-based care models, which focus on patient outcomes and cost efficiency. This shift aims to improve the quality of care by incentivizing healthcare providers to focus on the health outcomes of their patients rather than the number of services delivered. Patient-centricity has also become a core focus, with healthcare systems striving to provide care that is more responsive to individual patient preferences, needs, and values.
Regulatory Changes and Cybersecurity: Regulatory changes continue to impact the healthcare sector, with governments worldwide implementing policies to protect patient data, encourage interoperability, and ensure the ethical use of AI in healthcare. The rise of digital health technologies has also heightened the importance of cybersecurity, as the industry becomes increasingly vulnerable to data breaches and cyberattacks, prompting healthcare organizations to invest heavily in protecting patient information.
Cost Management and Accessibility: Despite advancements, managing healthcare costs remains a significant challenge, particularly in countries like the United States, where healthcare spending is notably high. There is a growing emphasis on finding innovative ways to reduce costs without compromising care quality, including preventive care initiatives, the adoption of generic medications, and optimizing of healthcare supply chains. Additionally, ensuring equitable access to healthcare services remains a pressing concern, especially in underserved and rural areas.
The Role of Big Data and Analytics: Big data and analytics play a critical role in healthcare transformation, offering insights that can lead to better patient outcomes, more efficient operations, and informed strategic decision-making. These technologies enable the analysis of vast amounts of health data, facilitating research, population health management, and the early detection of disease outbreaks.
Looking Ahead: The future of the healthcare industry is poised for further innovation and transformation. The ongoing integration of genomics and personalized medicine is expected to offer new frontiers in treatment options. Moreover, the industry will likely to see an expansion of AI applications, from drug discovery to patient care, and a greater focus on mental health, reflecting a more holistic approach to well-being.
In conclusion, the healthcare industry is navigating a period of significant change, driven by technological advancements, shifts in care delivery models, and the imperative to address cost and access disparities. As it moves forward, the industry’s ability to adapt to these changes while focusing on patient-centered care will be crucial for its success in meeting the health needs of populations worldwide.
Technology
The technology industry stands as a beacon of relentless innovation, growth, and transformation, fundamentally reshaping how we live, work, and interact. In the current landscape, several key trends and challenges are defining the trajectory of this dynamic sector.
Innovation and Disruption: The tech industry continues to be at the forefront of innovation, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, and quantum computing. AI and machine learning, in particular, are becoming ubiquitous, enhancing everything from consumer applications to complex business processes. Blockchain technology is gaining traction beyond cryptocurrencies, with applications in supply chain management, secure transactions, and identity verification. Quantum computing, though still in its infancy, promises to revolutionize industries by solving complex problems far beyond the reach of traditional computers.
5G and Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks is accelerating, promising to unlock new opportunities for the tech industry. This next-generation of wireless technology offers faster speeds, lower latency, and the capacity to connect many devices simultaneously. It is expected to enable breakthroughs in areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and smart cities, facilitating more seamless and interactive experiences.
Cybersecurity Challenges: As technology becomes more integrated into our daily lives, cybersecurity has become a critical concern. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks are prompting businesses and governments to prioritize security and invest in advanced protection measures. The industry focuses on developing more robust security frameworks, encryption technologies, and threat detection algorithms to safeguard digital assets and personal data.
Cloud Computing and Edge Computing: Cloud computing continues to be a major growth driver for the technology industry, offering scalable resources and infrastructure on demand. The evolution of cloud services is now seeing a complementary rise in edge computing, where data processing occurs closer to the data source. This shift is essential for real-time processing and analysis applications, such as streaming services, industrial IoT, and autonomous vehicles.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations: The environmental impact of technology operations, from energy consumption in data centers to the lifecycle of electronic devices, is under increasing scrutiny. The industry is responding with initiatives to improve energy efficiency, reduce waste, and promote recycling and sustainable materials. Moreover, ethical considerations around AI and data privacy are prompting discussions on regulation and the developing of ethical guidelines for technology development and use.
Remote Work and Digital Transformation: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technologies and the shift towards remote work, trends that are likely to persist. Businesses across sectors are undergoing digital transformation at an unprecedented pace, leveraging technology to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and enable a more flexible workforce. This shift is also drives demand for cloud services, collaboration tools, and cybersecurity solutions.
Consumer Technology Trends: In the consumer space, the technology integration into everyday life continues unabated. Wearable technology, smart home devices, and immersive experiences through augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are becoming more mainstream, driven by consumer demand for convenience, wellness, and enhanced experiences.
Looking ahead, the technology industry is poised for continued growth and innovation. Challenges such as cybersecurity threats and ethical concerns will require concerted efforts to address. However, the sector’s foundational role in driving progress across economies and societies remains undisputed. As it navigates these complexities, the industry will continue to shape the future, offering new solutions and opportunities that were once the realm of science fiction.
Non-Profit & Charities
The non-profit and charities sector is crucial in addressing societal challenges, providing essential services, and advocating for change across various issues, including poverty, education, health, environmental conservation, and human rights. Despite facing perennial funding, resource allocation, and operational efficiency challenges, the sector is currently undergoing significant transformations, driven by technological advancements, changing donor expectations, and the global context shaped by recent events like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Technological Integration: Non-profits increasingly adopt technology to enhance their operations, fundraising efforts, and outreach activities. Digital platforms, social media, and mobile apps are used to engage with a broader audience, share impact stories, and facilitate online donations. Furthermore, data analytics and artificial intelligence are helping organizations to optimize resource allocation, track program effectiveness, and identify areas requiring intervention. This technological shift improves operational efficiency and enables non-profits to achieve greater scale and impact.
Diversification of Funding Sources: Traditional funding models evolve as non-profits seek to diversify their revenue streams to ensure sustainability. This includes exploring social enterprise models, where non-profits create businesses to further their social or environmental goals while generating revenue. Crowdfunding and online giving have also become significant, particularly in mobilizing resources for immediate needs, such as disaster relief efforts. Additionally, there’s a growing emphasis on building long-term relationships with donors through regular communication and engagement strategies that highlight the impact of their contributions.
Increased Accountability and Transparency: Donors and stakeholders demand greater transparency and accountability from non-profits. This has led to the adopting more rigorous reporting standards and using technology to provide real-time insights into how funds are being used and the outcomes being achieved. Organizations also focus on impact measurement and evaluation to demonstrate their effectiveness and justify continued support.
Collaboration and Partnerships: There’s a growing recognition within the sector of the benefits of collaboration and partnerships. Non-profits increasingly work with governments, businesses, and other non-profits to amplify their impact. Such collaborations can provide access to additional resources, expertise, and networks, enabling more comprehensive approaches to complex issues.
Shifts in Volunteerism: Volunteerism is changing towards more skilled volunteering and virtual opportunities. Individuals seek ways to contribute their specific skills and expertise, while organizations are finding new ways to engage volunteers remotely, especially during the pandemic. This trend towards skill-based and remote volunteering is expands the pool of potential volunteers and allows non-profits to leverage a wider range of expertise.
Focus on Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI): The non-profit sector increasingly focuses on DEI within its operations, programming, and leadership. This reflects a broader societal push for equity and justice and recognizes the importance of diverse perspectives in effectively addressing social issues. Organizations are taking steps to ensure their staff, leadership, and board members reflect the diversity of their communities and that their programs are designed to be inclusive and equitable.
The non-profit and charities industry faces the challenge of adapting to a rapidly changing world while staying true to their mission and values. Embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and focusing on transparency and impact will be key to navigating these challenges. Despite the obstacles, the sector’s resilience and commitment to social good suggest a continued ability to make a significant difference in the lives of people and the planet.

Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry is currently navigating through a period of significant transformation and adaptation, shaped by technological advancements, shifting global supply chains, and evolving consumer demands. This dynamic landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for manufacturers worldwide.
Technological Advancements: The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies is at the forefront of the manufacturing industry’s evolution. This includes the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and additive manufacturing (3D printing) into production processes. These technologies are revolutionizing manufacturing by enhancing efficiency, productivity, and flexibility. Smart factories, characterized by their digital connectivity and automation, are becoming more prevalent, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of manufacturing processes.
Supply Chain Resilience: Recent global events, including the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions, have exposed vulnerabilities in the global supply chain. Manufacturers are responding by reevaluating and diversifying their supply chains to mitigate risks associated with reliance on single sources or regions. There’s an increasing emphasis on supply chain resilience, with strategies including nearshoring or reshoring of manufacturing operations to closer align production with key markets and reduce transportation costs and complexities.
Sustainability and Circular Economy: Environmental sustainability has become a critical focus for the manufacturing industry. Regulatory pressures and changing consumer preferences drive manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices and consider the environmental impact of their operations and products. This includes efforts to reduce waste, lower carbon emissions, and implement circular economy principles, where the goal is to design out waste, keep products and materials in use, and regenerate natural systems.
Workforce Development and Skills Gap: The manufacturing sector faces a significant skills gap, exacerbated by the retirement of a large portion of the workforce and the industry’s evolving technological needs. Attracting and retaining talent is a major challenge, prompting manufacturers to invest in training and development programs to upskill their workforce. There’s also a push to improve the industry’s image among younger generations, highlighting the technological innovation and opportunities for career growth within manufacturing.
Customization and Consumer Demand: Consumers increasingly seek personalized products, driving manufacturers to adopt more flexible production systems that can accommodate customization. This shift requires advanced manufacturing technologies and data analytics to efficiently manage the complexity and variability of customized production without compromising on speed or cost.
Global Competition and Market Dynamics: The manufacturing industry continues to be highly competitive, with companies vying for domestic and international market share. Emerging markets are increasingly important, not only as sources of low-cost production but also as growing consumer markets. Manufacturers must navigate these complex global dynamics, including trade policies and tariffs, to strategically position themselves in the market.
Digital Transformation: Beyond the factory floor, digital transformation is reshaping other aspects of the manufacturing business, from supply chain management to customer engagement. Digital tools and platforms enable manufacturers to enhance their operational agility, improve customer experiences, and create new business models.
In the future, the manufacturing industry’s future will be characterized by its ability to adapt to these ongoing changes. Success will depend on embracing technological innovation, building resilient supply chains, prioritizing sustainability, addressing the workforce skills gap, and responding to changing consumer preferences. Despite the challenges, these developments offer significant growth and transformation potential, positioning the manufacturing industry as a key driver of global economic progress and innovation.
B2B Service
The B2B (Business-to-Business) service industry is currently experiencing a dynamic phase of growth and transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving customer expectations, and the global shift towards digitalization. As businesses across all sectors seek to navigate the complexities of the modern market, the demand for specialized B2B services that offer efficiency, expertise, and technological solutions is higher than ever.
Technological Innovation: The rapid pace of technological innovation is a major force shaping the B2B service industry. Cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and blockchain are among the technologies revolutionizing how B2B services are delivered and consumed. These technologies enable service providers to offer thei clients more personalized, efficient, and secure services, ranging from IT and software solutions to logistics and supply chain management.
Digital Transformation: Digital transformation is a buzzword and a strategic imperative for B2B service providers. The move towards digital platforms allows for the automation of processes, enhanced data analytics capabilities, and more agile service delivery models. Companies are investing in digital technologies to improve their operational efficiency, customer service, and to develop new, innovative service offerings that meet the changing needs of their business clients.
Customer-Centricity: Today’s B2B service industry is increasingly customer-centric. There’s a growing recognition of the importance of understanding and meeting the specific needs of business clients, which has led to a focus on customization and flexibility in service offerings. Service providers are leveraging data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences, enabling them to tailor their services more effectively and enhance customer engagement and loyalty.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations: Sustainability and corporate social responsibility are becoming critical factors in the B2B service industry. Businesses are seeking service providers who deliver economic value and align with their environmental and ethical standards. This trend drives B2B service firms to adopt greener practices, promote ethical labor standards, and engage in social responsibility initiatives.
Globalization and Market Expansion: The B2B service industry is increasingly global, with companies expanding their reach to serve clients across different regions. This expansion is facilitated by digital technologies that enable service delivery across borders. However, global expansion also presents challenges, including navigating diverse regulatory environments and cultural differences in business practices.
The Rise of Subscription-Based Models: The subscription economy impacts the B2B service industry, with more companies offering their services through subscription-based models. This shift from one-time transactions to ongoing service relationships benefits for both providers and clients, including predictable revenue streams for providers and cost-effective, scalable solutions for clients.
Talent and Skills Gap: The demand for skilled professionals in the B2B service industry is growing, particularly in IT, cybersecurity, and data analytics. Companies face challenges in attracting and retaining talent, leading to increased investment in training and development programs, and a focus on creating more attractive and flexible work environments.
In conclusion, the B2B service industry is at a critical juncture, with significant opportunities for growth and innovation. Success in this evolving landscape requires a focus on technological advancement, customer-centric service models, sustainability, and attracting and retaining skilled professionals. As B2B service providers adapt to these trends, they are well-positioned to meet their business clients’ increasingly complex and specialized needs, driving value and efficiency across industries.
Locations
This service is primarily available within the following locations:

New York City NY
The economy of New York is one of the largest and most vibrant in the United States, reflecting a diverse and dynamic mix of industries, innovation, and a highly skilled workforce. As the financial capital of the U.S., New York City (NYC) anchors the state’s economy, with Wall Street’s stock exchanges and financial institutions playing a pivotal role in national and global finance. Beyond finance, New York’s economy is characterized by strong sectors in technology, media, healthcare, education, and tourism.
Financial Services: The financial sector is the cornerstone of New York’s economy. NYC is home to the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ, two of the world’s largest stock exchanges by market capitalization. This sector contributes significantly to the state’s GDP and employs many people in various positions, from banking and insurance to investment and financial analysis. The presence of major banks, hedge funds, and investment firms underscores the state’s global influence in finance.
Technology and Innovation: New York has emerged as a significant hub for technology and innovation, second only to Silicon Valley regarding venture capital investment and startup ecosystem strength. Tech companies in NYC, often referred to as “Silicon Alley,” span a range of industries, including fintech, health tech, and e-commerce. The state’s commitment to fostering innovation is also evident in its support for research and development, particularly in upstate New York, where technology parks and universities contribute to advancements in nanotechnology, clean energy, and biotechnology.
Media and Entertainment: The state is a global center for media and entertainment, housing major broadcasting networks, publishing houses, and advertising agencies. New York’s vibrant cultural scene, from Broadway theaters to film production, significantly contributes to the local economy, attracting talent and tourists alike. The media sector enriches the state’s cultural fabric and represents a substantial economic activity, generating thousands of jobs and promoting other industries through advertising and marketing.
Tourism: Tourism is a vital part of New York’s economy, with NYC being one of the most visited cities in the world. Attractions such as the Statue of Liberty, Central Park, and the Metropolitan Museum of Art, alongside events like Fashion Week and the New York Marathon, draw millions of visitors annually. The tourism industry supports numerous hospitality, retail, and entertainment jobs, and generates significant revenue through hotel bookings, dining, and shopping.
Healthcare and Education: New York is home to some of the world’s leading healthcare institutions and research centers, contributing to the state’s economy through innovation in medical research, patient care, and health education. The state’s numerous universities and colleges, including Ivy League schools like Columbia University and Cornell University, are not only centers of academic excellence but also major employers and contributors to the local economy through research, development, and the attraction of international students.
Manufacturing and Agriculture: While finance and technology dominate NYC’s economy, upstate New York has a strong manufacturing base, producing goods ranging from electronics to pharmaceuticals. Agriculture also plays a significant role, with New York being a major producer of dairy, apples, and wine, among other products. These sectors benefit from the state’s rich natural resources and contribute to the diversity and resilience of New York’s economy.
In conclusion, New York’s economy is multifaceted and robust, driven by a mix of traditional industries and emerging sectors. The state’s strategic location, skilled workforce, and innovative policies continue to attract investment and talent, ensuring its status as a leading economic powerhouse in the U.S. and globally. Despite challenges such as the high cost of living and doing business, New York’s economy remains dynamic, with a strong capacity for growth and adaptation.

Philadelphia PA
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, stands as a significant and historical economic hub in the United States, blending a rich heritage with a vibrant present. Its diversified economy has strong footholds in sectors such as healthcare, education, manufacturing, technology, and tourism, contributing to its resilience and growth.
Healthcare and Education: Philadelphia’s economy is notably anchored by the “eds and meds” sectors—education and healthcare— its largest employers. The city is renowned for its concentration of medical institutions and hospitals, such as the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, making it a leader in medical research and patient care. Additionally, Philadelphia’s numerous universities and colleges, including the University of Pennsylvania, Drexel University, and Temple University, bolster the city’s reputation as a center for academic excellence and contribute significantly to the local economy through employment, innovation, and attracting international students.
Manufacturing: Historically, Philadelphia has been a manufacturing powerhouse, and although the sector has declined since its mid-20th-century peak, it remains an important part of the city’s economy. Today’s manufacturing focuses on advanced and specialized products, including chemicals, medical devices, and food products. The sector benefits from the city’s strategic location, access to transportation networks, and industrial parks that facilitate production and distribution.
Technology and Innovation: The technology sector in Philadelphia is growing, with the city increasingly being recognized as an emerging hub for startups and innovation. This growth is supported by the city’s strong educational institutions, which foster talent and research, and a collaborative business environment that encourages entrepreneurship. Tech firms in Philadelphia are making strides in health tech, biotech, and fintech, contributing to the city’s economic diversification and modernization.
Tourism: Tourism is a vital part of Philadelphia’s economy, driven by its rich historical significance, cultural institutions, and vibrant food scene. Iconic landmarks such as the Liberty Bell, Independence Hall, and the Philadelphia Museum of Art attract millions of visitors annually. The sector supports a wide range of hospitality, retail, and entertainment jobs, and generates significant revenue for the city.
Financial Services: The financial services sector, including banking, insurance, and investment, plays a crucial role in Philadelphia’s economy. The city’s financial institutions support the broader regional economy through lending, investment, and financial management services. Philadelphia’s strategic location also makes it a convenient hub for business services, supporting professional and corporate services.
Real Estate and Development: Philadelphia’s real estate market has been experiencing growth, driven by residential and commercial development. The city’s efforts to revitalize neighborhoods, improve infrastructure, and attract businesses have contributed to a dynamic real estate sector. This growth is supported by relatively affordable housing compared to other major cities, attracting individuals and companies to the area.
Challenges and Opportunities: Like many urban centers, Philadelphia faces challenges, including addressing income inequality, enhancing public education, and improving infrastructure. However, the city’s economic diversity, strategic location, and rich cultural and educational assets present numerous opportunities for growth and development.
In conclusion, Philadelphia’s economy is multifaceted, with healthcare, education, technology, and tourism strengths. The city’s historical significance, and its modern economic drivers, positions Philadelphia as a key player in the broader financial landscape of the Northeastern United States. Leveraging its diverse economic base and fostering innovation will be crucial for Philadelphia’s continued growth and resilience.

Baltimore, MD
Baltimore, Maryland, possesses a dynamic and diverse economy, characterized by a rich maritime history, a strategic location along the Eastern Seaboard, and a robust foundation in healthcare, education, and biosciences industries. Despite facing economic challenges, including income disparity and the need for urban revitalization, Baltimore’s economy demonstrates resilience and potential for innovation and growth.
Healthcare and Education: Baltimore is distinguished by its world-renowned healthcare and educational institutions, with Johns Hopkins University and its medical system being the city’s leading employers. These institutions are pivotal in providing healthcare services and education and play a significant role in research and development, particularly in medicine and public health. The presence of these institutions contributes significantly to the local economy through job creation, innovation, and attracting international students and healthcare professionals.
Port of Baltimore: The Port of Baltimore is a key asset to the city’s economy, serving as one of the busiest ports in the United States. It plays a crucial role in international trade and logistics, handling a diverse range of cargo, including automobiles, bulk commodities, and containers. The port’s efficiency and strategic location contribute to Baltimore’s status as a significant transportation and distribution hub, supporting jobs in logistics, shipping, and related industries.
Biosciences and Technology: Baltimore has made concerted efforts to position itself as a center for bioscience and technology innovation, leveraging the research output of its universities and healthcare institutions. The city has seen growth in biotech startups and companies, driven by support from academic, government, and private sector partnerships. This sector promises high-value job creation and the potential for significant contributions to both the local and national economy.
Financial Services and Professional Services: The financial and professional services sectors are also vital to Baltimore’s economy, encompassing banking, legal services, and consultancy firms. These industries benefit from the city’s educated workforce and proximity to major East Coast markets, including Washington, D.C., and New York City.
Tourism: Tourism is an important economic driver for Baltimore, with the city’s rich history, cultural attractions, and waterfront developments drawing visitors. Attractions such as the Inner Harbor, the National Aquarium, and historical sites related to the city’s maritime heritage and its role in American history contribute to the local economy through hospitality, retail, and entertainment.
Manufacturing: While manufacturing in Baltimore has declined from its historical peaks, the sector remains an important part of the economy. Efforts to modernize and diversify manufacturing include focusing on advanced manufacturing techniques and developing industries related to green technology and sustainable practices.
Challenges and Opportunities: Baltimore faces several economic challenges, including high unemployment rates in certain areas, income inequality, and the need for urban revitalization. However, there are also significant opportunities for economic development through continued investment in healthcare, education, and technology sectors, as well as initiatives to leverage the city’s geographical advantages and historical assets.
In conclusion, Baltimore’s economy is marked by a blend of traditional industries and emerging sectors, with significant strengths in healthcare, education, and biosciences. The city’s strategic location and rich institutional base provide a strong foundation for future growth. Addressing existing economic disparities and focusing on sustainable urban development are key to ensuring Baltimore’s financial resilience and prosperity.
Boston, MA
Boston, Massachusetts, stands as a beacon of economic strength and innovation in the United States, underpinned by its rich historical roots, prestigious educational institutions, and a forward-looking approach to industry and technology. This vibrant city’s economy is diversified and resilient, marked by significant contributions from the education, healthcare, finance, technology, and biotechnology sectors.
Education and Research: Boston’s economy is deeply influenced by its world-renowned academic institutions, including Harvard University, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and Boston University, among others. These institutions not only draw students from across the globe but also foster a culture of research and innovation, contributing to the city’s economy through education services, research grants, and the creation of a highly skilled workforce. The academic environment fuels the city’s robust ecosystem of startups and research and development in various fields, particularly in technology and life sciences.
Healthcare and Biotechnology: The city is a global leader in healthcare and biotechnology, home to cutting-edge hospitals and research facilities like Massachusetts General Hospital and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. This sector attracts significant investment and talent, driving innovation in medical research, pharmaceuticals, and biotech startups. The concentration of these institutions supports not only healthcare delivery but also medical research and the commercialization of new medical technologies and therapies, contributing substantially to Boston’s economy.
Technology and Innovation: Boston’s economy is characterized by a strong tech sector, with significant activity in software, hardware, and emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and clean energy. The city’s culture of innovation, supported by its academic institutions and a dynamic venture capital scene, makes it an attractive location for startups and established tech companies. This environment fosters job creation and positions Boston as a competitive player in the global technology market.
Finance: The financial services sector, including banking, investment management, and insurance, is another cornerstone of Boston’s economy. The city is home to major financial institutions and investment firms, contributing to its reputation as a leading financial hub. This sector provides employment opportunities and supports the broader regional economy through capital allocation and financial management services.
Tourism: Tourism also plays a vital role in Boston’s economy, with the city’s rich history, cultural institutions, and sports teams attracting visitors worldwide. Landmarks such as the Freedom Trail, the Museum of Fine Arts, Fenway Park, and the historic neighborhoods of Boston draw millions of tourists annually, supporting a vibrant hospitality industry.
Real Estate and Development: Boston’s real estate market is robust, and driven by demand in the residential and commercial sectors. The city’s growth and economic vitality have led to significant real estate development, including expanding the Seaport District and redeveloping historic areas. This growth, however, also presents challenges, including housing affordability and the need for sustainable urban planning.
Challenges and Opportunities: Like many urban centers, Boston faces challenges related to income disparity, housing affordability, and infrastructure needs. Addressing these issues is critical to ensuring the city’s continued prosperity and quality of life for its residents. Additionally, Boston’s emphasis on innovation, education, and healthcare positions it well to capitalize on future economic opportunities, particularly in technology and biotechnology.
In conclusion, Boston’s economy is dynamic and multifaceted, driven by its education, healthcare, technology, and finance strengths. The city’s blend of historical significance and commitment to innovation creates a unique environment that fosters economic growth and development. As Boston continues to evolve, its ability to leverage its educational and technological assets while addressing social and economic challenges will be key to its future success.

Pittsburgh, PA
Once the heart of America’s steel industry, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, has transformed into a vibrant and diversified economy. This transition is a testament to the city’s resilience and ability to innovate. Today, Pittsburgh’s economy is driven by healthcare, education, technology, finance, and advanced manufacturing, showcasing a remarkable evolution from its industrial past.
Healthcare and Education: Pittsburgh’s economy is significantly bolstered by the healthcare sector, with some of the city’s largest employers in this field, including the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC). This institution is a leading healthcare provider and a major contributor to medical research, making significant advancements in organ transplantation, psychiatry, and neurology. The education sector, led by institutions such as the University of Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University, is another cornerstone of the local economy. These universities are centers of innovation and research, contributing to the workforce’s skills and attracting students and professionals from around the globe.
Technology and Innovation: Over the years, Pittsburgh has emerged as a hub for technology and innovation. The city has capitalized on its strong academic base to foster growth in robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and software engineering. Companies like Google, Uber, and Facebook have established significant operations in Pittsburgh, drawn by the talent pool and the innovative research in robotics and AI at Carnegie Mellon University. This focus on cutting-edge technology has helped revitalize the city’s economy, creating jobs and attracting investment.
Advanced Manufacturing: While the steel industry no longer dominates, manufacturing remains an important part of Pittsburgh’s economy. The city has shifted towards advanced manufacturing, leveraging new technologies to produce high-value goods in aerospace, robotics, and biomedical devices. This evolution reflects Pittsburgh’s ability to adapt to global economic changes, maintaining its manufacturing heritage while embracing innovation.
Finance: The finance sector is also critical in Pittsburgh’s economy. The city is home to major financial institutions such as PNC Financial Services, contributing to the region’s economic stability and growth.These companies offer various financial services, supporting the local economy and clients nationwide.
Energy: Pittsburgh’s economy benefits from its location in the Marcellus Shale region, one of the largest natural gas fields in the United States. The energy sector, including natural gas extraction and related services, has become a significant economic driver, contributing to job creation and investment in the region. However, the city also focuses on sustainable energy solutions, reflecting a commitment to environmental stewardship and innovation.
Tourism: Tourism is an increasingly important part of Pittsburgh’s economy, with the city’s rich cultural scene, sports teams, and historic sites attracting visitors. The revitalization of the downtown area and the development of attractions such as the Andy Warhol Museum and the Pittsburgh Cultural District have enhanced the city’s appeal as a tourist destination.
Challenges and Opportunities: Despite its economic transformation, Pittsburgh faces challenges, including population decline and the need for further diversification of its economy. Addressing affordable housing, infrastructure improvement, and creating more inclusive economic opportunities will be crucial for the city’s continued growth and prosperity.
In conclusion, Pittsburgh’s economy is a model of resilience and innovation, having successfully transitioned from an industrial powerhouse to a modern, diversified economy. The city’s strengths in healthcare, education, technology, and manufacturing, combined with its commitment to innovation and sustainability, position Pittsburgh for continued economic success in the 21st century.
Program Benefits
Marketing
- Data-Driven Insights
- Customer Segmentation
- Content Optimization
- ROI Measurement
- Predictive Analytics
- Customer Engagement
- Competitor Analysis
- Campaign Optimization
- Email Marketing
- Creative Testing
Operations
- Inventory Management
- Process Automation
- Maintenance Predictions
- Quality Control
- Resource Allocation
- Cost Reduction
- Logistics & Distribution
- Risk Management
- Vendor Management
- Sustainability Initiatives
Human Resources
- Talent Acquisition
- Employee Onboarding
- Performance Management
- Learning & Development
- Employee Engagement
- Retention Strategies
- Workforce Planning
- Compensation Analysis
- HR Analytics
- Wellness Programs
Testimonials

“You helped us grow from $4.5 Million to $17 Million.”
– Warren, NYC Commercial Construction Company, New York, NY

CEO Software Company
“Mr. McAdam’s Corporate Growth with AI program is a must-have for any business looking to stay ahead in the digital era. Mr. McAdam’s unique insights and proven strategic alternatives helped us unlock the full potential in our market while using AI as a resource. We’ve seen remarkable improvements in our business performance and are confident that our investment in Mr. McAdam’s program will continue to pay dividends for years.”
I can’t believe it took us this long to engage Mr. McAdam, but I’m so happy we did. The numbers don’t lie.”

Adam Education Services CEO, Chicago, IL
“My management team is now invigorated, focused, and ready for accelerated growth, and we already see results. Now I have to say, ‘Whoa! Instead of Sick ‘em!’ Also, keep doing those one-on-one meetings with executives before joining as a group. It helps everyone get on the same page quickly.”

Image Processing Company, Division President, Ohio
“Mr. McAdam’s Corporate Growth workshops were a game changer for our business. His insights and focus helped us use strategic planning by leveraging AI to streamline operations, improve customer engagement, and drive revenue growth. We highly recommend this program to any company looking to stay competitive and grow in the digital age.”

Sign Painting Company, Philadelphia, PA
“The workshops were wonderful. I didn’t want them to end. They helped me project and build my business future. I am so grateful for the results. I don’t know what would have been more effective.”

EVP, Shareholder, East Coast Transportation Company
“Your workshops played a small but powerful role in helping us grow our EBITDA for a successful exit. And it wasn’t as hard as I thought it would be.”
More detailed achievements, references and testimonials are confidentially available to clients upon request.
Client Telephone Conference (CTC)
If you have any questions or would like to arrange a Client Telephone Conference (CTC) to discuss this particular Unique Consulting Service Proposition (UCSP) in more detail, please CLICK HERE.












